- Home
-
Solutions
-
Leak Seal
Seal leaks in concrete or masonry with crack injection and curtain grouting of our Prime Flex polyurethanes and AR acrylate resins. Prime Resins offers superior solutions for stopping leaks in every type of environment.
Read More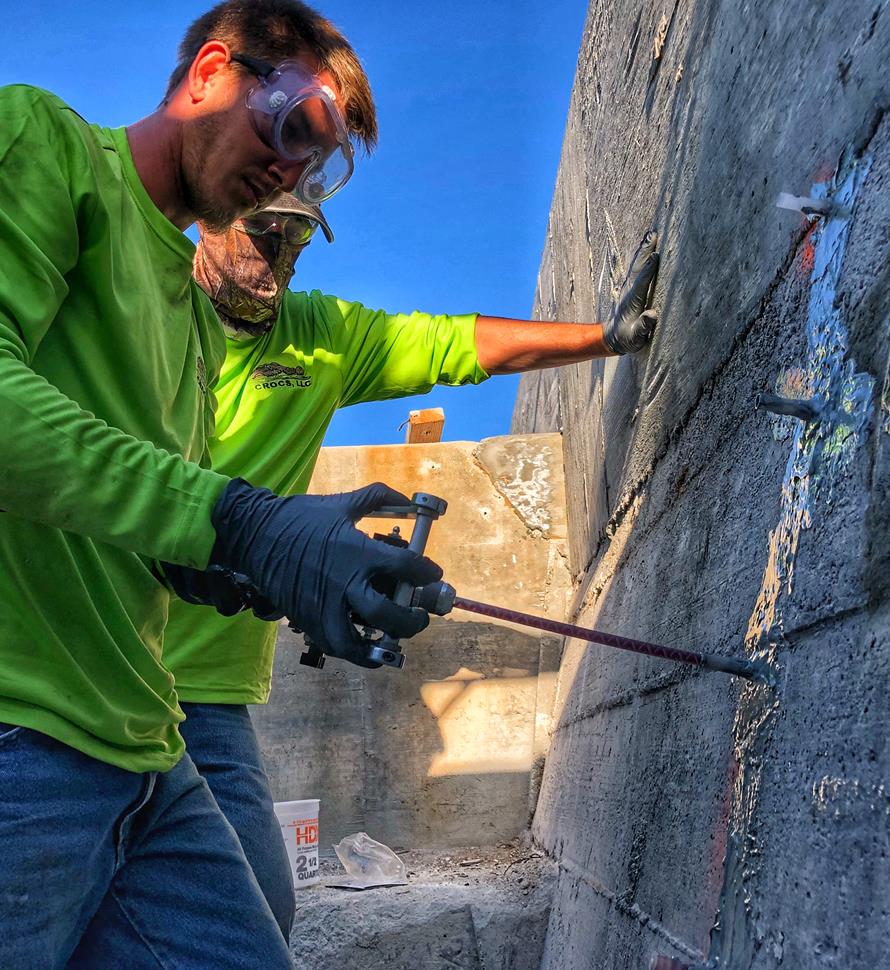
-
Soil Stabilization
Sound concrete relies on a sound substrate. Stabilize soils and fill voids with our polyurethane and acrylate foams and gels. We make chemical grouts for permeation and compaction grouting in wet and dry conditions.
Read More
-
Slab Lifting & Stabilization
Slab lifting and slab stabilization with polyurethane foams offers many advantages over traditional mudjacking. Only Precision Lift is engineered to tackle underlying issues and slab lifting with precise, dependable results.
Read More
-
Floor Repair & Joint Protection
Spalled concrete is concrete that is chipped, cracked and deteriorating. This often happens at a joint.
Read More
-
Seawall Repair
You can repair a seawall or bulkhead with Prime Resins chemical grouts: fill voids, stabilize loose soil and seal leaks at a fraction of the cost of wall replacement.
Read More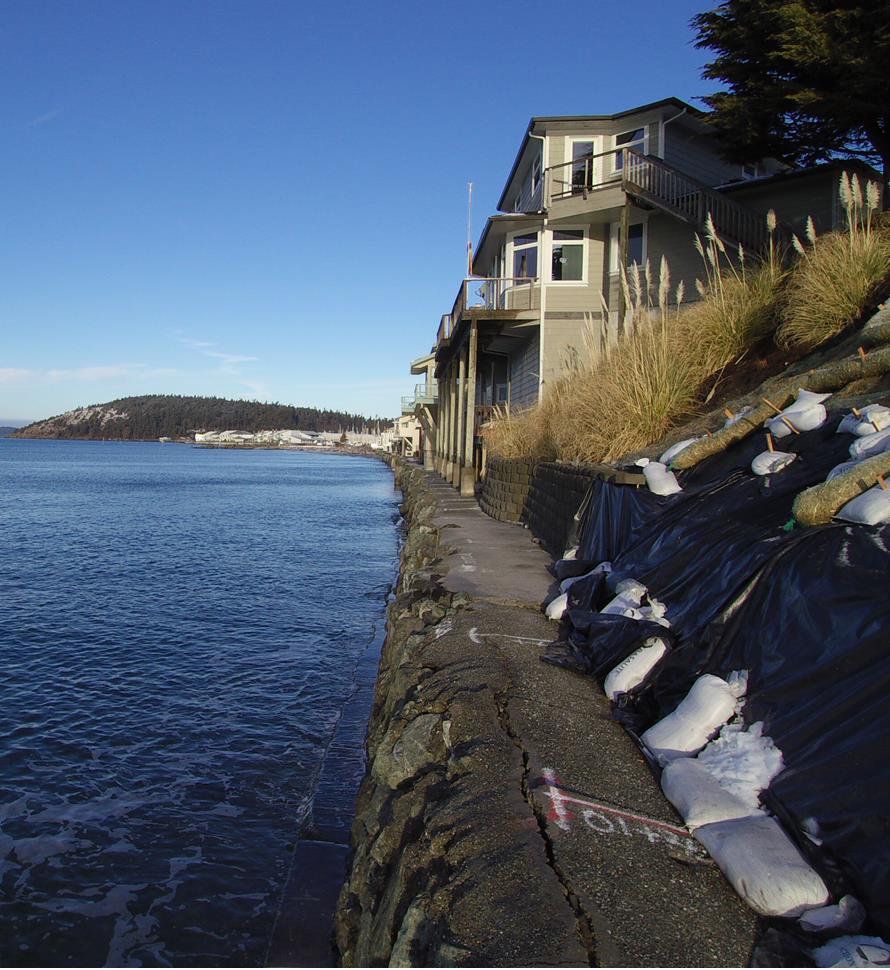
-
Structural Repair / Bonding & Anchoring
The need for crack repair in concrete structures can be caused by many different factors. Damage can occur to the concrete in situations where direct impact puts stress on one area of the structure.
Read More
-
Highway & Bridge
The geotechnical needs of DOTs and other agencies responsible for roads and bridges are vast. Issues include: Culvert repair Soil stabilization Void filling Concrete slab lifting Sinkhole remediation Slope control Slough control in tunneling
Read More
-
Waterproofing & Secondary Containment
Protecting concrete usually means shielding it from the elements of nature or from harsh manmade chemicals. But it’s not just concrete that needs such protection. Corrugated metal pipe, steel surfaces, material hoppers, rail cars and masonry all can come in contact with corrosive or abrasive materials or harsh conditions.
Read More
-
Leak Seal
-
Products
-
Leak Repair
- AR 800
- Conduit Seal Kit
- PR10L ACLM
- Soakum Oakum Kit
- Prime Flex 900 XLV
- Prime Flex 910
- Prime Flex 920
- Prime Flex 940
- Prime Flex 985 LX10
- Prime Flex 985 LX20
- Prime Flex 985 5.0
- Prime Flex 985 5.0 Fast
- Prime Flex Hydro Gel™ SX
- Prime Plug 1, 2 & 3
- PrimeCem MSM
- PrimeCem CAM
- PR10 ACLM (granular)
- Prime Flex Hydro Gel™ EXP

-
Soil Improvement

- Soil Stabilization
- Slab Lifting
- Structural Repair / Bonding & Anchoring
- Pumps
- Dispense Guns & Applicators
-
Turnkey Trailer Rig
Are you ready to hit the ground running doing concrete leveling with polyurethane foam? Prime Resins offers the industry’s best suite of products for lifting concrete as a turnkey, fully equipped trailer rig.
Read More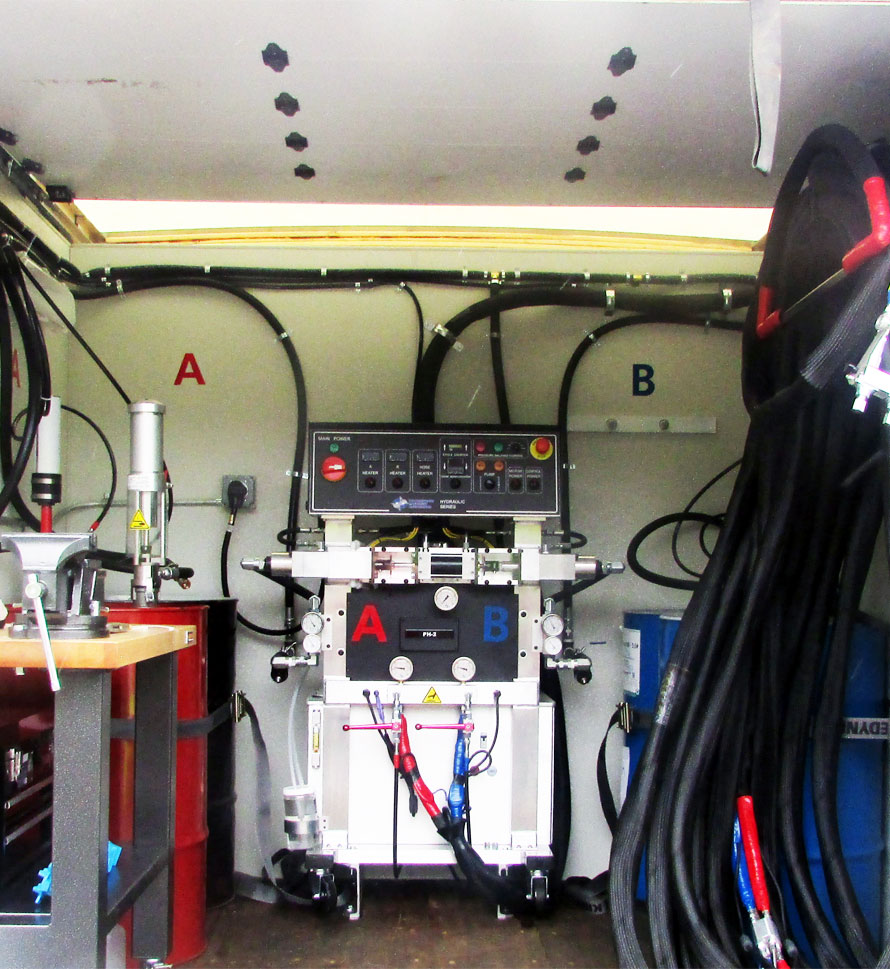
-
Accessories (General)
- 3/4" expendable drive point
- 3/8" and 3/4" soil probes
- Cartridge / Port Connectors and Mixers
- Conduit Seal Kit
- Eco Flush
- F Valve
- Flush Wand
- Grout Needle Kit
- High Pressure Control Valve
- High Pressure Mechanical Ports
- Kick Fast
- Low Pressure Plastic Ports
- PR11 TEA (used w/ PR10 ACLM)
- PR12 APSF catalyst (used w/ PR10 ACLM)
- PR17 LYTX
- Prime Kat
- Prime Plug
- Prime Solvent CGC
- Oakum
- Soil pipe jack
- Stainless Steel Grout Needle & Kit
- StainShield
- Wall Stinger Nozzle
-
Soil Grouting Accessories
- Pipe Coupler
- Pipe Coupler Ferrule
- Buttonhead Coupler - Straight
- Buttonhead Fittings
- SG 3/4" Expendable Drive Tip
- SG 3/4 Rod - 39" Base
- SG 3/4 Rod - 39" Connector
- SG 3/4 Rod - 19.5" Base
- SG 3/4 Rod - 19.5" Connector
- SG 3/4 Fitting - Pipe to Buttonhead
- SG 3/4 Fitting - Buttonhead Fitting
- IL 1/2" Drive Point
- IL 1/2" rod - 39" base
- IL 1/2" rod - 39" connector
- IL 1/2" Fitting Buttonhead
- SG 3/4" Fitting - Buttonhead Coupler
- SG 3/4" Slotted Drive Tip
- SG 3/4 Drive Head
- Modified Pipe Jack Soil Grouting
- SG 3/4 Fitting - Buttonhead Coupler
- Pagani DPM30 Penetrometer
- IL 1/2" Fitting - Buttonhead to Connector Rod
- IL 1/2" Rod to Rod Coupler Fitting
- High Pressure Flow Control Valve
- Buttonhead Coupler - 90°
- Buttonhead Clamp Kit
- DPM30 Penetrometers
- JackJaw Soil Probe Extractor
- Floor & Joint Repair
- Waterproofing & Secondary Containment
-
Leak Repair
- News
- Downloads
-
Tools
-
Case Studies
Prime Resins takes pride in its ability to find the right solutions to the problems facing our customers. Here are some examples of customers’ successful jobs:
Read More
-
Prime Practices

-
Videos

-
Estimating Tools & Info.

-
Why us?
The superior quality of products at a fair price, our consultative approach, and our unparalleled technical support set Prime Resins apart. Learn more about the Prime difference.
Read More
-
Product Types & Typical Uses

-
Looking for a contractor?
-
Certifications
-
Podcasts
-
Case Studies
- Contact

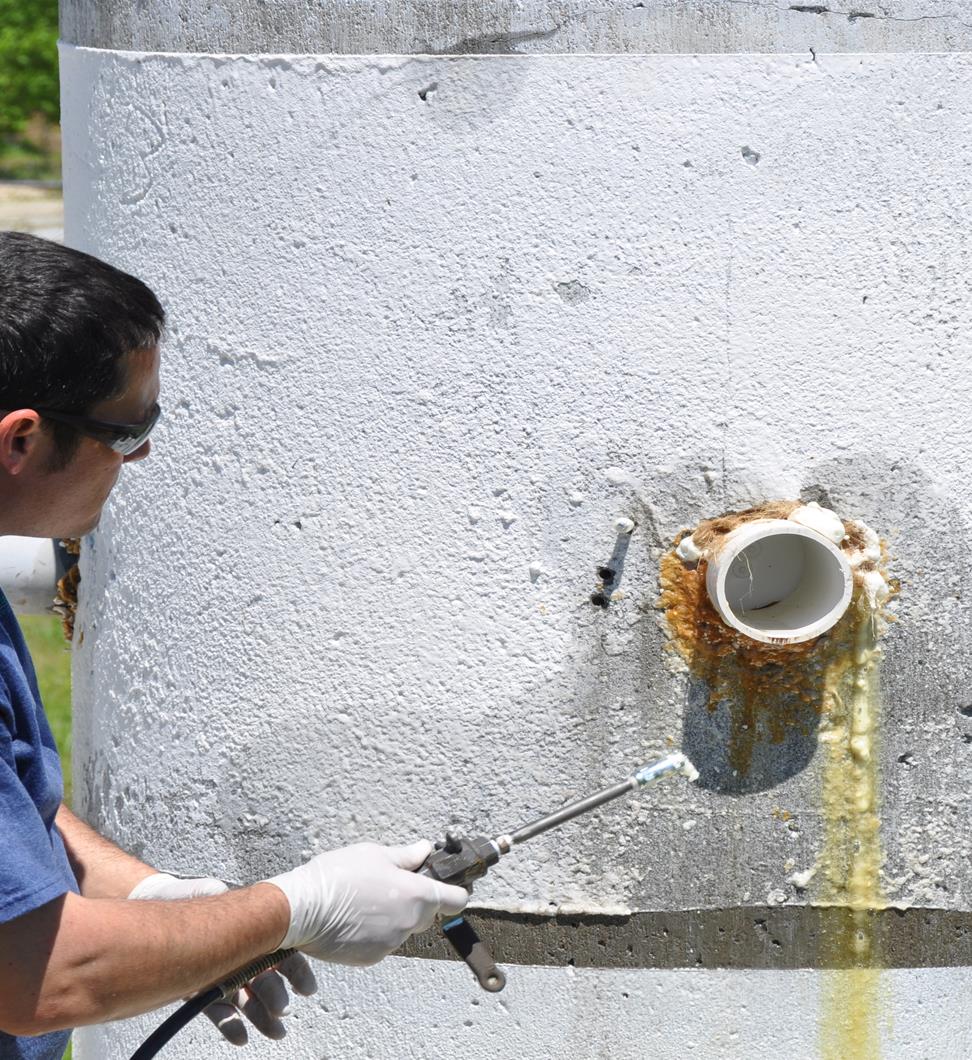
Prime Practices
910 Probe Grouting Seawalls and Bulkheads
Scope of Work: Probe injection of Prime Flex 910 or 920 behind a seawall or bulkhead
Problem:
There is a leak in the seawall or bulkhead that causes soil loss. As the tide comes in or waves hit the wall, water penetrates the wall, soaking the substrate behind the wall. As the water recedes, it takes soil with it, creating voids. Perhaps there is a gap under the footer where soil erodes, undermining the seawall.
Solution:
Prime Flex 910 or 920 structural polyurethane chemical grouts seal active leaks in seawalls, fill voids, and stabilize the soil behind it.

STEP ONE: SOIL ANALYSIS
Complete a soil analysis and probe for voids. The contractor may need this to determine proper probe placement and to identify potential problem areas and natural differences in soil composition. Prior to injecting, ensure that soils contain enough moisture to fully react the grout OR use a plural-component pump to inject water and grout simultaneously (twin streaming) through injection pipe/probe.
NOTE: Void filling generally requires twin streaming if a large volume of grout is needed. This ensures activation of all grout, not just what first contacts moisture in the soil. Twin streaming also yields a more consistent and uniform foam throughout.
When twin streaming, use a ratio of 10:1 grout:water.
We recommend a pump capable of injection pressures from 100 psi – 2500 psi. The flow rate of pumps should be .33 gpm minimum. Manually operated or hand pumps are unacceptable. Do not use a manual pump.
STEP TWO: DETERMINE PROBE SPACING
Determine appropriate spacing and depth placement for injection probes to successfully seal, stabilize and fill the area as shown in drawings. Test sections may be necessary to determine the best probe spacing depending on soil types and conditions encountered.
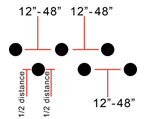
Typical spacing will vary between 12” – 48” in each direction and if multiple rows are needed, then each row shall be offset half the space distance.
Use Prime Resins soil probes or expendable drive points to keep dirt from clogging the pipe during driving. Pipes may be placed by a manual driver, a pneumatic driver, auger, water jetter or other method approved by the engineer prior to placement.
STEP THREE: TEST CATALYST LEVELS
For soil grouting: To determine the best ratio of catalyst to grout, gather three one-gallon containers of compacted soil typical of the injection area and prepare three eight-ounce samples of grout.
One sample of grout should be catalyzed with 1% catalyst, the second with 3% catalyst, and the third with 5% catalyst. Make a hole approximately 2” in diameter extending three-fourths of the distance to the bottom in the center of each compacted soil sample.
Pour one mixture of catalyzed grout into the center hole in each soil sample. Press the soil back
over the hole and allow the grout to cure for approximately 15 minutes. After the material has cured,
dump out the contents of the containers and determine which mixture of grout and catalyst has produced the best pattern of migration.
STEP FOUR: DETERMINE AMOUNT OF GROUT NEEDED
Determine the amount of grout needed for each probe to ensure all locations within the work
area are fully grouted. Check for voids using a probe. Grout using the “Lift Grouting Technique”
where the pipe is raised or jacked up and grout is injected in 12”-18” intervals or lifts. The contractor should determine the amount of grout injected at each lift based on soil conditions for that area. Injection pressures will vary depending on soil conditions. We provide a void calculator here.
NOTE: Grouting seawalls can also be done via the “through wall” method. This involves drilling holes through a wall (or footer) and grouting via these holes. Please reference the “Curtain grouting through wall” Prime Practice.
STEP FIVE: PUMP UNTIL REFUSAL
Continue pumping to the point of refusal and you see grout sealing the wall through to the water side. Be sure to use a floating debris boom to capture any reacted polyurethane foam in the water.

STEP SIX: CLEAN OUT OR INSTALL WEEP HOLES
Ensure that weep holes/drain holes are free of grout at the completion of the project. If no weep holes
exist, install a drain hole with a filter; such as a Jet filter or similar product.
Safety Considerations:
To ensure a safe work environment, all equipment used should meet or exceed OSHA (or comparable in other countries) safety requirements.
Materials List:
– Prime Flex 910 or Prime Flex 920. The latter is NSF/ANSI Standard 61 compliant.
– Prime Kat catalyst
Equipment List:
– Pump
– 3-4 empty clean 5-gallon pails
– Personal safety equipment (gloves and eye protection)
– Soil probes
– Expendable drive point
– Floating boom
Related Content:
– Wooden bulkhead repair (Magnolia, TX)
– Rock seawall repair (Anacortes, WA)
– Seawall repair saves big bucks (Palm Beach, FL)
– Seawall Repair, Void Fill – 920 (Lake Harris, FL)
– Seawall Repair, Void Fill – 920 (Delray Beach, FL)
– Seawall Repair – 920 (Lake Park, FL)
– Seawall Repair – 910 (Ft. Lauderdale, FL)









